Mussels: Everything You Need To Know
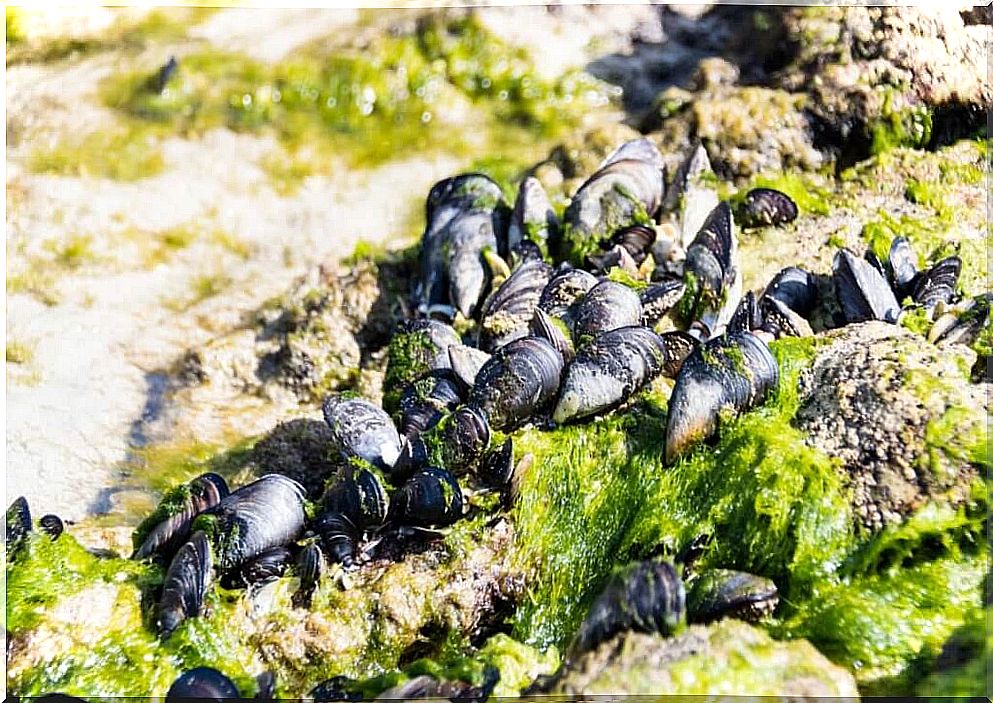

Mussels or Mytilids ( Mytilidae ), are a family of molluscs protected by a 2-part shell and that live attached to the rocky shores of the sea. This taxonomic grouping comprises 52 different genera.
The mussel family is quite old, as many studies confirm its existence since the Devonian period. In prehistoric times, clam shells were used by North American Indians as tools, says Tom Suchanek – a doctor of fish and conservation biology.
Currently, mussels are of great interest as food and as biomonitors of the quality of coastal waters. Learn more about the life of these bivalve molluscs in the following lines.
General features
Male mussels (genus Mytilus ) are light orange in color and females are darker. The color of the shells that protect its body is black, with shades of purple, blue or brown, as indicated by the Junta de Andalucía .
Seafood experts say these invertebrates often form colonies around the world, especially in colder seas. Still, species that live in fresh water and others that prefer warmer seas have been found.
Thanks to the byssus – a substance expelled by the mussel that takes the form of filaments – the mussels can attach themselves to rocks or other surfaces submerged in the sea. That’s why we always see them tied to the bottom of the sea, unmoved by the waves and currents.

Mussel feeding and breeding
The shells that protect the mussels are slightly open, so there is always a constant flow of water inside the mussel. The waves promote the constant renewal of the water around them, which increases their food and oxygen, as they are nourished by phytoplankton and organic matter, according to the newspaper El País .
Its reproduction occurs when the right conditions exist in terms of food and temperature. Mussels live huddled on rocks, very close to each other, and this proximity is very important when it comes to reproduction.
When the time comes, the male releases his sperm in the form of a thread that, thanks to the movement of the sea, is taken inside the female. In a few minutes, the female releases a large quantity of fertilized eggs in the form of spheres, which become part of planktonic life and then fix on other surfaces to transform into mussels.
appreciated consumption
In recent years – according to the Spanish Association of Economic History – mussels have undergone a process of globalization in their production. Since the 1970s, one of the main exporting and producing countries has been Spain. However, in recent decades, new countries that grow and export mussels have emerged, such as Chile.
Mussels are appreciated for their flavor and nutritional properties, as their consumption promotes health and prevents disease. They are low in fat, rich in protein and, in addition, they are used in the preparation of a wide variety of delicious dishes.
They are a natural source of omega 3, vitamin B12, iron, phosphorus and zinc. They help in the normal growth and development of children’s bones, contribute to cognitive development and promote fertility and reproduction, according to the informative newspaper Faro de Vigo . With this information, it is clear to us that mussels are excellent foods.
The mussels currently
Phytoplankton – the staple diet of mussels – can currently be accompanied by plastic residues due to pollution and the large amount of accumulated residues. The diet of these molluscs is being contaminated and this can cause their death, experts say.
It used to be easier to find mussels in the sea, but due to marine pollution, invasive species, acidification of the sea and global warming, the existence of these invertebrates has decreased in many of the planet’s waters.

Mussels are not only of great gastronomic value to humans, they act as debris filters and universal seawater purifiers. It is essential to preserve them, as without them, an invaluable part of the food chain of aquatic ecosystems is lost.